
Section 19 (Judge)
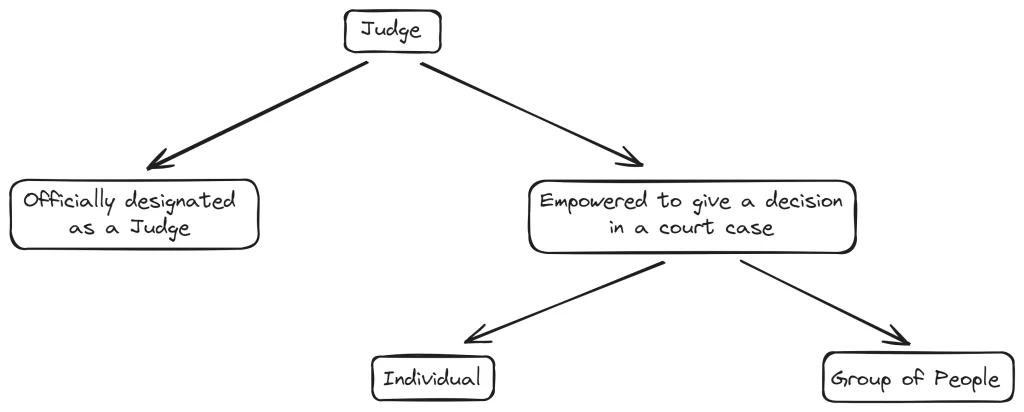
The word “Judge” refers to not only people who are officially called Judges, but also to anyone who has the legal power to make a final decision in a court case.
There are a few types of people who are considered Judges:
- A person who is officially designated as a Judge, like a District Judge or High Court Judge.
- Anyone empowered by law to give a decision in a legal proceeding (court case). This decision could be civil (non-criminal) or criminal. If the decision is not appealed, it becomes final. Or if another authority confirms the decision, it becomes final.
- A member of a group of people empowered by law to give a final decision. For example, a panel of Judges on a court.
Illustrations
(a) A Collector is someone who collects taxes. When a Collector is handling a legal case under Act X of 1859, they are acting as a Judge for that case.
(b) A Magistrate is a legal officer with powers to investigate crimes and handle related legal matters. When a Magistrate is dealing with a criminal charge where they have the authority to punish with a fine or imprisonment, with or without the option for appeal, they are acting as a Judge in that situation.
(c) A Magistrate is only considered a Judge when they can fully handle and decide a criminal case themselves. If a Magistrate can only investigate a charge and then has to send the case to another court for actual trial, they are not regarded as a Judge for that particular matter.
Section 21 (Public servant)
[Military, crimes, imprison, judges, Jury, arbitrators, court, election, tax]
- Commissioned officers in the military, navy or air force of Bangladesh.
- Government officers whose work involves preventing crimes, informing of crimes, catching criminals, or protecting public health, safety or finances.
- People who have the power to confine or imprison others due to their job.
- Judges and people who perform judicial functions.
- Jury members, assessors or panchayat members assisting courts or public servants.
- Arbitrators or others referred cases or issues for decision by courts or authorities.
- Officers working in courts of law who investigate matters, authenticate documents, handle property or execute legal processes.
- People empowered to prepare, publish, maintain or revise electoral rolls or conduct elections or parts of elections.
- Officers responsible for villages, towns or districts — doing surveys, tax assessments, collecting rates or taxes, or maintaining documents for residents’ rights.
- Officers handling government property, doing surveys, assessments or contracts for the government, executing revenue work, investigating government financial matters or making related documents.
Illustrations
• A Municipal Commissioner is considered a public servant because they work for a local government authority.
• Anyone employed by the government or paid by the government through fees or commissions for public work is a public servant.
• Anyone employed by or paid by a local authority, corporation established by law, or company where the government has interest or shares, is a public servant.
• Whether a public servant is formally appointed by the government or not does not matter – what matters is the job/role they hold.
• Wherever “public servant” is mentioned, it refers to anyone actually doing that job, even if there are flaws in how they hold that position.
• The word “election” means any process by which members of public authorities like legislative bodies, municipal boards etc. are selected through voting as prescribed by law.
Section (23+24+25)
Section 23 (Wrongful gain; Wrongful loss; Losing wrongfully)
- “Wrongful gain”
- “Wrongful gain” refers to illegally obtaining something valuable that does not rightfully belong to the person getting it.
- ইল্লিগ্যালি একশন এর মাধ্যমে গেইন করা হয়েছে।
- যে গেইন করেছে সে, সেই জিনিসটির রাইটফুল ওউনার না।
- “Wrongful gain” refers to illegally obtaining something valuable that does not rightfully belong to the person getting it.
- “Wrongful loss”
- “Wrongful loss” means losing or being deprived of something valuable that you legally own or have rights over, but losing it through unlawful or illegal means.
- ইল্লিগ্যালি একশন এর মাধ্যমে ছিনিয়ে নেয়া হয়েছে।
- যে হারিয়েছে সে, সেই জিনিসটির রাইটফুল ওউনার ছিলো।
- “Wrongful loss” means losing or being deprived of something valuable that you legally own or have rights over, but losing it through unlawful or illegal means.
- “Gaining wrongfully”
- Acquires wrongfully.
- Retains wrongfully.
- “Losing wrongfully”
- Wrongfully kept out of any property.
- Wrongfully deprived of property.
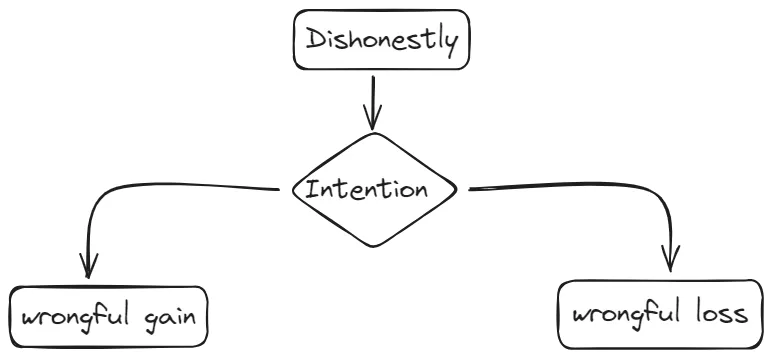
Section 24 (Dishonestly)
Whoever does anything with the intention of causing wrongful gain to one person or wrongful loss to another person, is said to do that thing “dishonestly”.
– Intention of causing wrongful gain.
– Intention of causing wrongful loss
Section 25 (Fraudulently)
When someone intentionally does something to deceive others and gain an unfair advantage, it is considered fraudulent. However, if they do that thing without any intention to defraud, it is not considered fraudulent.
- Intention to deceive.
Section 34: Acts done by Several Persons in Furtherance of Common Intention
When a crime is committed by a group of people together, with all of them having the same intention, then each person involved in the group can be held responsible for the crime in the same way as if they had committed the crime alone.
- Group of people.
- Same intension.
- Deemed to have committed the crime alone.
Section 52 (Harbour)
- Except for specific cases mentioned in section 157 and section 130 when the spouse provides the Harbour.
- In general, “harbour” includes actions like providing someone with a place to stay, food, drinks, money, clothes, weapons, transportation, or helping them in any way to avoid getting caught, regardless of the methods used.






